
Role Of Telehealth Services In Achieving Quadruple Aim of Healthcare
Role Of RPM Services In Achieving Quadruple Aim of Healthcare It’s no secret that delivering top-notch healthcare is becoming more challenging daily. We’re talking about

The health landscape is taking an arbitrary shift, and the fusion of technology with medical science has revolutionized the way healthcare providers approach health and wellness. One such interdisciplinary field that is making waves in the healthcare industry is Informatics in Healthcare. At its core, healthcare informatics sits at the intersection of information technology and healthcare, aiming to enhance the quality of patient care and health outcomes.
Whether it is the usage of EHR, Remote Patient Monitoring Devices, or Telemedicine, the common goal they share is to make a meaningful difference in the way healthcare is managed. But what does it mean in the context of medical and clinical practices? All these questions and more will be answered in this blog. So stay connected.
Informatics, at it’s essence, refers to the science of applying principles of IT to the advancement of research, clinical practice, and management of healthcare as a whole. It relates to the application of data analytics, medical knowledge, health information technology, artificial intelligence (AI), and communication systems to improve patient care.
Informatics in healthcare applies that same approach in the realm of medicine: it’s about using computers and other digital tools to collect data on patients’ health history and apply the data to a larger pool of information, enabling healthcare providers to gain greater insights into individual patient care.
Health Informatics is an interdisciplinary professional field that utilizes the use of biomedical data and information in scientific inquiries, medical problems, and decision-making, all centered on improving the patient’s health outcomes.
The application of health informatics is widely spread apart from improving patient outcomes and management of health services. They may include

Many get confused between health informatics and health information technology. They often surface, sometimes used interchangeably.
Health Informatics: This is a broader field that utilizes the principles of information and computer science to improve healthcare delivery. it’s not about the technology but how technology is used, how data is collected, analyzed, and transformed into actionable insights, and how these insights influence clinical decisions, policies, and patient care.
Health Information Technology (Health IT): This, on the other hand, refers more specifically to the actual tools and software used in the collection, storage, and exchange of health information. EHRs, digital billing systems, telehealth platforms, and patient management software are all examples of Health IT.
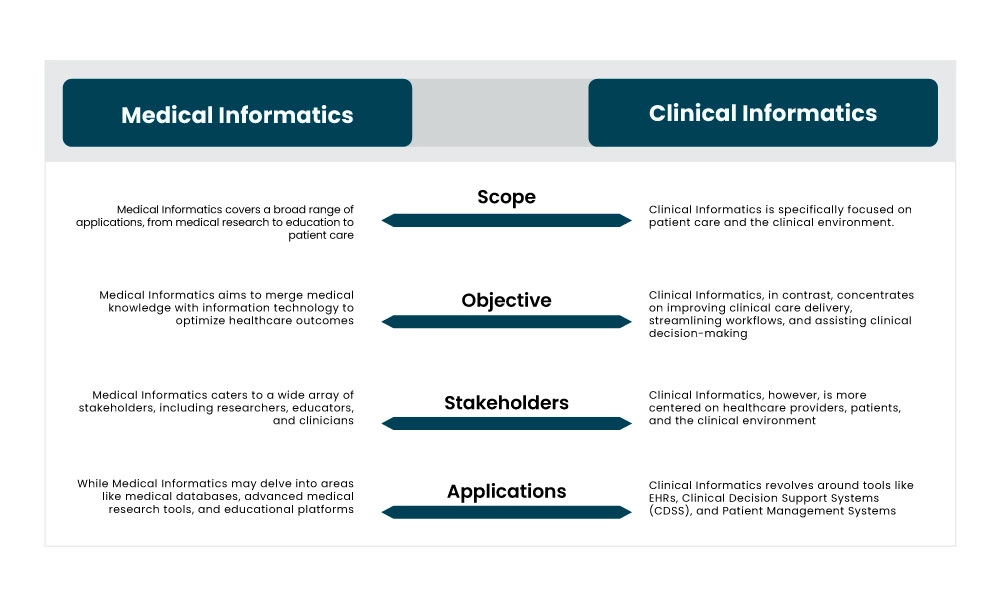
Medical Informatics can be described as the interdisciplinary study that focuses on the design, development, and optimization of computerized systems in healthcare. It encompasses a broad scope of intersecting computer science, cognitive science, and health sciences to enhance medical research, education, and patient care.
Key areas include the development of computerized medical records, medical databases, clinical decision support tools, and health information systems. It’s about applying informatics principles to medical knowledge, emphasizing the entire healthcare continuum, from data acquisition to its application in medical settings.
Clinical Informatics, on the other hand, narrows its focus primarily to the application of informatics principles in clinical settings. It concentrates on tools and methodologies that improve patient care delivery, supporting the clinical decision-making process, and streamlining workflows in healthcare environments.
This field is deeply entrenched in the day-to-day operations of healthcare facilities. Clinical informaticists often work on refining Electronic Health Records (EHRs), ensuring they are user-friendly, enhancing patient-clinician communication, and integrating various systems to provide coordinated care.
Nursing Informatics is defined as the integration of nursing, its information and knowledge, with information and communication technologies to promote the health of people worldwide. It’s a domain that recognizes the vital role nurses play in patient care and seeks to enhance their practice through the effective use of technological tools and data management.
At its core, Nursing Informatics aims to improve patient care outcomes by ensuring that nurses have access to relevant, timely, and accurate information. It provides the tools and methodologies that allow nurses to capture, retrieve, and analyze data, transforming it into actionable knowledge.
Public Health Informatics can be defined as the application of information science and technology to public health practice, research, and learning. Unlike clinical informatics, which focuses on individual patient care, Public Health Informatics is all about populations. It strives to improve the health outcomes of communities, regions, or entire nations by effectively collecting, analyzing, and applying health data on a large scale.
Informatics in Healthcare is a vast and diverse field that encompasses a range of disciplines, from medical informatics to nursing informatics to public health informatics. It’s about using advanced technology and data analysis tools to improve patient outcomes, streamline clinical workflows, and advance healthcare research. By leveraging the power of information science, informaticists are transforming healthcare into an increasingly efficient, effective, and accessible industry.
Ultimately, it’s all about improving the lives of patients around the world through thoughtful application of technology and analytics. This is no small task; it requires expertise and dedication from many different stakeholders. But with the right tools and resources, informaticists can make a real difference in healthcare delivery across the globe.

Role Of RPM Services In Achieving Quadruple Aim of Healthcare It’s no secret that delivering top-notch healthcare is becoming more challenging daily. We’re talking about

What is Cost Containment in Healthcare: How to Achieve it with Telehealth The rising cost of healthcare is a pressing concern that resonates deeply
Talk to an Expert Now