

For the more than 61 million Americans living in rural communities, the phrase “lack of proximity” can be an all too familiar challenge when it comes to healthcare. Miles of open road often separate rural residents from specialists, hospitals, and critical medical services.
However, a technological revolution is quietly transforming the landscape of rural healthcare: telehealth. This innovative approach to care delivery is bridging the gap between patients and providers, offering a lifeline to those in remote areas who once faced daunting barriers to accessing quality medical attention.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into how telehealth is revolutionizing rural healthcare, exploring its benefits, addressing the unique challenges it presents, and highlighting inspiring success stories from communities across the country.
The stark reality of healthcare disparities in rural America is undeniable. As per the CDC, residents of rural communities face a higher risk of premature death from the leading causes, including heart disease, cancer, and stroke, compared to their urban and suburban counterparts. This disparity underscores a critical need for innovative solutions to bridge the gap in healthcare access and outcomes.
Numerous studies and real-world cases have proven the effectiveness of telehealth and remote patient monitoring (RPM) in achieving these goals. For rural residents, the ability to connect with healthcare providers virtually is transformative. It eliminates the barrier hindering in care allowing patients to access specialist consultations, chronic disease management, and even urgent care without the burden of lengthy travel or time away from work.
The increasing need for telehealth in rural communities is driven by a combination of factors, including:
While telehealth holds immense promise for revolutionizing rural healthcare, its implementation is not without its challenges. These obstacles often stem from rural communities’ unique characteristics and require thoughtful consideration and innovative solutions.
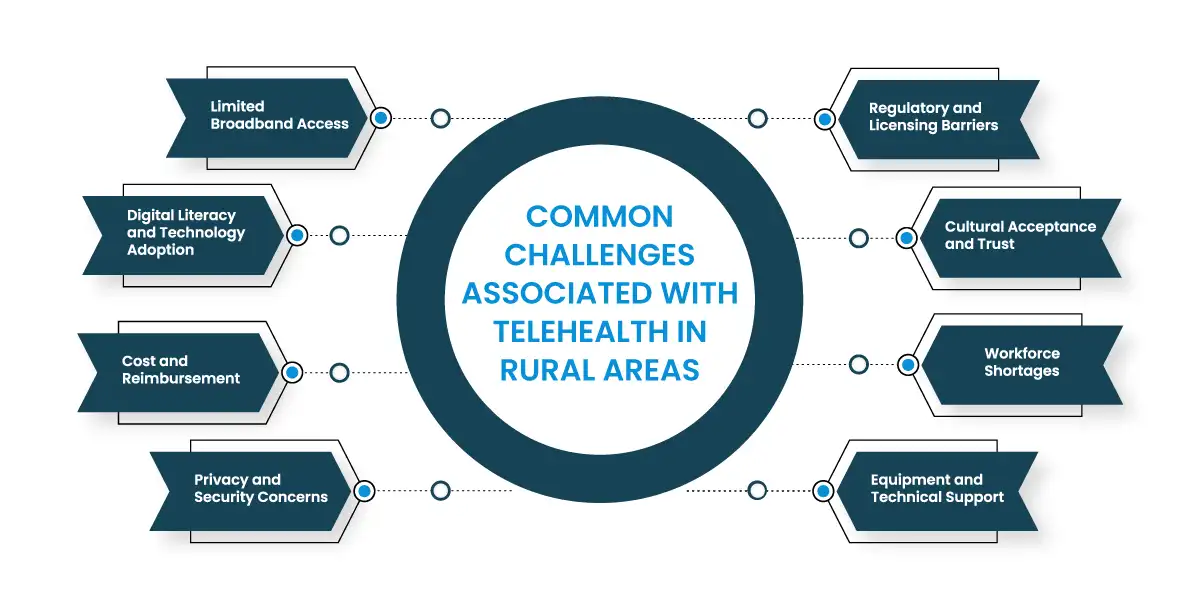
Limited Broadband Access
Reliable high-speed internet is the backbone of telehealth. Unfortunately, many rural areas lack adequate broadband infrastructure, hindering the quality and feasibility of virtual visits, data transmission, and remote patient monitoring.
Digital Literacy and Technology Adoption
Not all rural residents are tech-savvy or comfortable using digital devices and platforms. This can pose a barrier to accessing and utilizing telehealth services effectively.
Cost and Reimbursement
While telehealth can be cost-effective in the long run, initial investments in equipment, software, and training can be substantial for small rural healthcare providers. Additionally, reimbursement policies for telehealth services are not always consistent or adequate, creating financial challenges for both patients and providers.
Privacy and Security Concerns
Protecting patient privacy and ensuring the security of sensitive health data are paramount in any healthcare setting. However, maintaining robust cybersecurity measures can be challenging in rural areas with limited IT resources.
Regulatory and Licensing Barriers
Telehealth regulations and licensing requirements vary across states, creating a complex landscape for providers who wish to offer services across state lines. This can limit access to specialists and specialized care for rural patients.
Cultural Acceptance and Trust
Building trust in telehealth can take time in rural communities where traditional face-to-face interactions with healthcare providers are deeply ingrained. Educating patients about the benefits and safety of telehealth is crucial for fostering acceptance.
Workforce Shortages
Rural areas often face shortages of healthcare professionals, including those with expertise in telehealth technologies. Recruiting and retaining qualified staff is essential for successful telehealth implementation.
Equipment and Technical Support
Maintaining and troubleshooting telehealth equipment can be difficult in remote areas with limited access to technical support. Ensuring reliable equipment and providing ongoing technical assistance are vital for uninterrupted service delivery.
Rural healthcare providers face unique challenges in delivering quality care to their communities. Limited resources, geographic isolation, and workforce shortages can hinder their ability to meet the diverse needs of their patients. Telemedicine emerges as a transformative solution. There are a multitude of benefits of telehealth in rural areas that can address these challenges and reshape the landscape of rural healthcare.
Improved Access to Care
Telemedicine breaks down the barriers of distance, allowing patients in remote areas to access specialist consultations, chronic disease management, mental health services, and even urgent care without the need for lengthy travel. This not only improves convenience for patients but also reduces missed appointments and delayed care, leading to better health outcomes.
Enhanced Patient Engagement
Telemedicine empowers patients to actively participate in their healthcare. Virtual visits, remote monitoring, and online portals provide convenient ways for patients to communicate with their providers, access medical records, and receive personalized education, fostering a sense of ownership and engagement in their health journey.
Expanded Service Offerings
Rural providers can leverage telemedicine to expand their range of services beyond their immediate capacity. By partnering with specialists in urban centers or utilizing telemedicine platforms, they can offer consultations, diagnoses, and even procedures that were previously inaccessible to their patients.
Increased Efficiency and Cost Savings
Telemedicine streamlines healthcare delivery by reducing the need for in-person visits, minimizing administrative overhead, and optimizing resource utilization. This can lead to cost savings for both providers and patients, making healthcare more affordable and sustainable.
Attracting and Retaining Healthcare Professionals
Telemedicine can be a powerful recruitment tool for rural healthcare providers. It allows them to offer flexible work arrangements, collaboration opportunities with specialists, and exposure to a wider range of cases, making rural practice more appealing to healthcare professionals.
Improved Population Health Management
Telemedicine enables providers to proactively monitor and manage the health of their patient population. By tracking chronic conditions, identifying high-risk individuals, and delivering targeted interventions, they can prevent complications, reduce hospitalizations, and improve overall population health outcomes.
Enhanced Emergency Response
Telemedicine can play a crucial role in emergency situations in rural areas. Virtual consultations with specialists can guide local providers in delivering critical care, while remote monitoring can help stabilize patients before transport to a higher level of care if needed.
Staying Competitive:
As telemedicine becomes increasingly prevalent, rural providers who embrace this technology will be better positioned to compete with larger healthcare systems and attract patients seeking convenient and accessible care options.
Recognizing the unique challenges and opportunities faced by these communities, various government agencies and initiatives have been instrumental in driving the adoption of telemedicine through funding, policy development, and infrastructure support.
Collaboration and Partnerships:
The government also plays a crucial role in fostering collaboration between stakeholders, including healthcare providers, technology companies, and community organizations, to address the complex challenges of implementing telehealth in rural areas. This includes facilitating partnerships, sharing best practices, and promoting innovative solutions to improve access to care.
The integration of telehealth in rural healthcare is not merely a trend, but a transformative force that holds the potential to reshape the landscape of healthcare delivery in underserved communities. By addressing the unique challenges faced by rural residents and providers, telemedicine offers a path toward a more equitable, accessible, and efficient healthcare system for all.
For rural providers seeking to implement or enhance their telehealth programs, consider partnering with Global Touch LLC. Our comprehensive Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) and Chronic Care Management (CCM) solutions can streamline your workflow, improve patient engagement, and deliver exceptional care to your community.
Talk to an Expert Now