
Value Based Healthcare Demystified: What You Should Know
Value Based Healthcare Demystified: What You Should Know Ever since the reform made by CMS in care models, one phrase that you may have heard

Electronic health records are considered to be a great advancement in the healthcare field. Early in 1965, they were used to store patient information and were used as a way to keep track of medical records.Today, electronic health records have evolved into much more than just a storage system. In fact, they act as a central hub for all patient data, making it easier for healthcare professionals to access and share information. Interoperability is the key factor that makes this type of integration possible. So what is interoperability, and what are its implications? Let’s dive into the details and discover the significance of interoperability in healthcare.
In simple terms, interoperability is defined as the ability of different systems to work together seamlessly. In healthcare, it refers to the exchange and sharing of patient data across various electronic health record (EHR) systems, regardless of their differences in technology or vendors. This allows for a more comprehensive view of a patient’s medical history, making it easier for healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding their care.
In 2009, When the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act was put into action, it required all healthcare providers to adopt electronic health records in order to receive Medicare or Medicaid incentives. This move significantly increased the usage of EHRs and made interoperability a crucial aspect of modern healthcare.
Patients nowadays don’t receive care from a single healthcare provider. Instead, they are likely to receive care from multiple providers and specialists throughout their lifetime. In such a scenario, interoperability plays a crucial role in ensuring that the patient’s medical information is accurately and efficiently shared among different healthcare providers.
Interoperability gained immense importance during COVID-19 when data sharing among different healthcare systems became an essential requirement. Due to more and more home care treatments, healthcare professionals require easy access to patient records in order to provide optimal treatment.
We can have a better idea with this example scenario :
Let’s say a patient is admitted to an emergency room in another state. The healthcare providers at the ER would need access to that patient’s medical history, allergies, medications, and other vital information in order to provide appropriate care. In this case, interoperability allows for the seamless sharing of this information among different systems and ensures that the patient receives prompt and accurate treatment.
Interoperability in healthcare isn’t a one-size-fits-all concept; it occurs at different levels and in varying complexities. Understanding these levels is crucial for healthcare providers, policymakers, and technology developers to build and implement systems that are truly interoperable. Generally, there are Four recognized levels of interoperability in healthcare:
To better understand what is copay in insurance, let’s look at an example. If your insurance plan has a $20 copay for doctor visits, you pay that amount each time you visit the doctor, regardless of the total cost of the service.
Foundational interoperability allows for the one-way exchange of data between systems. This level of interoperability ensures that data sent from one system can be received by another. However, it doesn’t require the receiving system to interpret the data. This is the most basic level, where the focus is mainly on the transfer of data.
For example, a lab system may send test results to a hospital’s EHR. The hospital’s EHR receives and stores the data, but the system doesn’t necessarily understand or process the information further.
This level goes a step beyond by ensuring that the data structure is preserved and unaltered during the exchange between systems. Structural interoperability focuses on the format and organization of the data exchange, including items such as nesting and data types.
Imagine a scenario where a patient’s blood test results are shared from a laboratory’s system to a hospital’s EHR system. In this case, structural interoperability ensures that specific fields in the laboratory system map accurately to specific fields in the hospital’s EHR, allowing for more organized and efficient data use.
Semantic interoperability represents the highest level of interoperability. Here, the systems can not only exchange data but also interpret, use, and present the data in a way that’s meaningful to the end-user. This is enabled through common data models and vocabularies.
For instance, if a patient has an EHR that includes a history of allergic reactions to certain medications, semantic interoperability ensures that this critical information is not just transferred but also flagged in an understandable and actionable manner for healthcare providers in different settings. This helps in avoiding medical errors and enhances the quality of care.
Apart from the above three levels, organizational interoperability is also an important aspect of healthcare interoperability. It focuses on the policies, procedures, and agreements in place for data sharing between different organizations. This level ensures that there are clear guidelines and processes in place for the secure exchange of patient information.
Healthcare Information Technology (HIT) plays a crucial role in enabling interoperability within the healthcare system. It refers to the use of technology and information systems to store, manage, and share patient health information. HIT includes electronic health records, telehealth services, health information exchanges, and other digital tools that support the delivery of healthcare.
HIT has revolutionized the way healthcare is delivered, making it more efficient and accessible. With the increasing demand for interoperability, HIT continues to evolve and improve, enabling seamless data exchange among different systems.
EHR interoperability refers to the ability of different electronic health record systems to communicate and exchange data with one another. This is crucial in ensuring that patient information can be accessed, shared, and used by different healthcare providers and facilities. EHR interoperability allows for the integration of patient data from different sources, providing a comprehensive view of their health history.
Despite the numerous benefits of interoperability, there are still challenges that need to be addressed for successful implementation. These include:
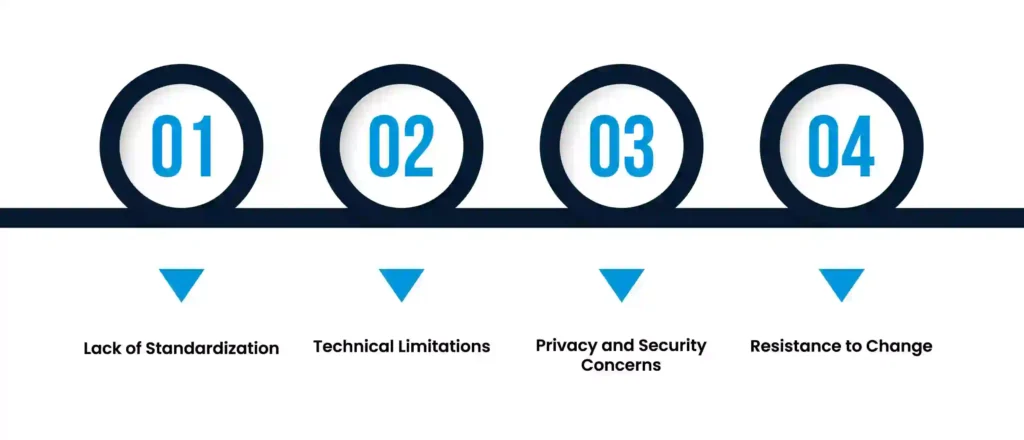
At Last, interoperability is crucial in ensuring a seamless and efficient healthcare system. It allows for the secure exchange of patient information, leading to improved care, cost savings, and innovation.
While there are challenges to achieving full interoperability, efforts are being made to address them and move towards a more connected healthcare landscape. As technology continues to evolve, so will interoperability, further enhancing the delivery of healthcare services.
Thus, interoperability in healthcare is not just a buzzword but an essential aspect of modern healthcare that benefits patients, providers, and the entire healthcare system. Let’s continue to work towards achieving full interoperability and improving the quality of care for all. So, let us embrace technology and strive towards a more connected and efficient healthcare ecosystem.

Value Based Healthcare Demystified: What You Should Know Ever since the reform made by CMS in care models, one phrase that you may have heard

How do telehealth and RPM help to reduce healthcare costs? The challenge of reducing healthcare costs is an ongoing battle for every healthcare provider. In
Talk to an Expert Now